

#Gonorrhea symptoms plus#
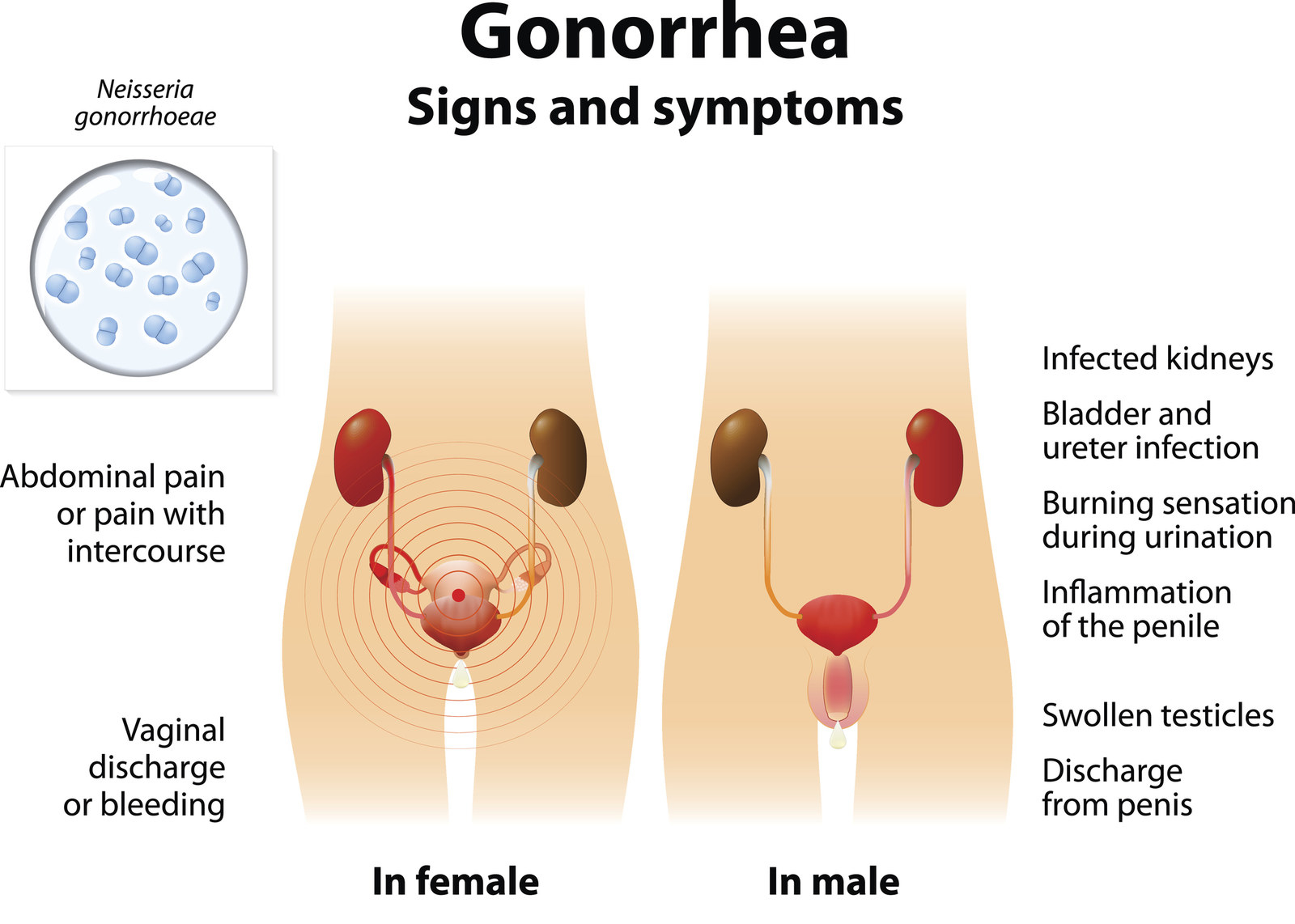
The usual treatment is a single injection of an antibiotic medicine plus a single large dose of a different antibiotic taken by mouth. Men who have sex with men can get infections of the back passage (anus) and throat.Rarely, a narrowing (stricture) of the urethra may develop.It may also cause infection of the testicles or the tubes around them ( epididymo-orchitis). In a small number of cases the infection travels up the urethra to the prostate gland.Rarely, there can be spread in the bloodstream to other parts of the body.Abscesses can develop in the Bartholin's glands on either side of the lower part of the vaginal opening.Pelvic infection can spread to the liver.Infection present during pregnancy can lead to infection spreading to the eyes of a newborn baby.Pregnancy can be complicated by premature labour, ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage.This can cause long-standing (chronic) pelvic pain and can lead to infertility. Infection can spread to the womb (uterus) to cause pelvic inflammatory disease.Are there any possible complications from gonorrhoea? What are the long-term effects of gonorrhoea? It will also be suggested that any sexual partners attend for tests and/or treatment. You will also be advised to have tests for other STIs. Another swab is taken from the inside the neck of the womb (the endocervix) at the womb's entrance. In women, a swab is taken from high up in the vagina. If a swab is taken for a man, it will be taken from the inside end of the penis (the urethra). A urine test is not as accurate in women as it is in men. Ideally you should attend a local GUM clinic for this.Ī urine sample and/or a sample (swab) of the discharge will be taken to try to identify the germ (bacterium) that causes gonorrhoea. You will normally be advised to have tests if gonorrhoea is suspected - even if symptoms go. Local and national information is also available on the internet - for example, from the Family Planning Association's 'Find a clinic' service. You can ring your GP, local hospital or health authority and ask where the nearest clinic is. In the UK you can go to the local GUM clinic without a referral from your GP.

If you suspect that you have gonorrhoea or any other STI then contact your local genitourinary medicine (GUM) clinic or see your GP. Sexual health blood and urine profiles now available in Patient Access Book now Do I need tests? However, without treatment, some germs (bacteria) usually remain in the urethra. This may take up to six months but can be just a couple of weeks or so. The symptoms may clear over time, even without treatment. However, about 1 in 2 women with gonorrhoea do not have any symptoms. Gonorrhoea is believed to cause symptoms in most infected men (about 9 in 10 affected). Such infections do not usually cause symptoms, although occasionally rectal pain, discharge or itching or a sore throat may be noticed. Infection of the back passage (rectum) or throat (pharynx) can develop.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
